NASA's Manned Space Vehicles

Project Mercury
Project Mercury was NASA's first program and ran from 1959 to 1963. The goal of the Mercury Program was to orbit the Earth in a manned spacecraft, investigate man's ability to function in Space, and recover both man and spacecraft safely. On May 5, 1961, Alan Shepard boarded Mercury 3, atop a Redstone Rocket and became the first American man in space. To accomplish their goals, NASA scientists conducted many rocket missions. The program was declared a success when in 1962 astronaut John Glenn became the first American to orbit the earth. When NASA ordered the vehicles for this project from McDonnell Aircraft, it started a new industry on the east coast of Florida. The longest and last Mercury mission was 34 hours long. The Mercury program is also responsible for the development of the Launch Escape System (LES) providing a safe egress for astronauts.
Mercury Space Craft
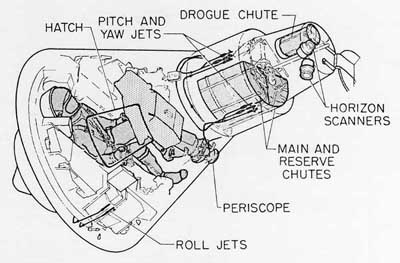
The mercury space craft was a tiny cone like capsule that was designed to carry one passenger. It had 120 different controls. There were three jets that allowed adjustment of roll, pitch and the yaw. The pilots were able to use any of the controls fueled from two different fuel tanks. So they were able to adjust the position of the space craft.
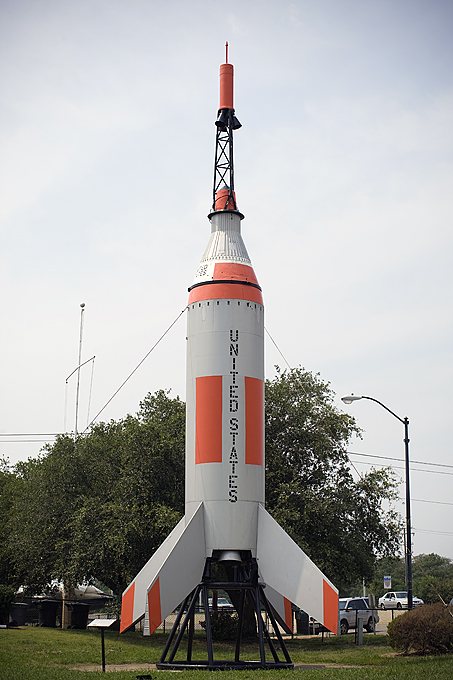
Mercury Little-Joe Rocket
The mercury space craft was a tiny cone like capsule that was designed to carry one passenger. It had 120 different controls. There were three jets that allowed adjustment of roll, pitch and the yaw. The pilots were able to use any of the controls fueled from two different fuel tanks. So they were able to adjust the position of the space craft.
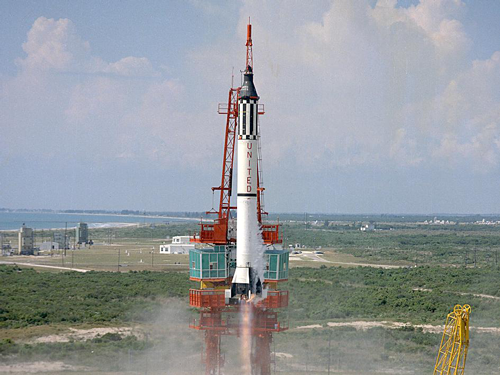
Mercury Redstone Rocket
The Mercury-Redstone Launch Vehicle, designed for NASA's Project Mercury, was the first American manned space booster. It was used for six sub-orbital Mercury flights from 1960–61.
Mercury Atlas Rocket
Atlas is a family of U.S. space launch vehicles. The original Atlas missile was designed in the late 1950s and produced by the Convair Division of General Dynamics, to be used as an intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM). It was a liquid-fuel rocket burning liquid oxygen and RP-1 in three engines configured in an unusual "stage-and-a-half" or "Parallel Staging" design. This engine configuration consisted of two outboard booster engines which were jettisoned during ascent, while its center sustainer engine, fuel tanks and other structural elements were retained into orbit.
← Manned Space Vehicles Overview Project Gemini →
The light hitting the earth right now is 30 thousand years old.