Timeline of Key Events during the US Space Program
Use your mouse wheel to scroll the timeline up and down, or select the year you would like to view on the menu found at the left of the page.
1957
October 4, 1957
Project Vanguard was managed by the United States Research Laboratory (NRL) and intended to launch the first artificial satellite into orbit using a Vanguard rocket from the Cape Canaveral Missile Annex.
Project Vanguard Launched - Universal Newsreel - 1957-12-09 Satellite A Bust (License: Creative Commons)
Project Vanguard Launched (License: Creative Commons WM)
November 1957
Explorer program was relaunched in response to the surprise Soviet launch of Sputnik 1.
1958
January 31, 1958
United States launches Explorer I from Cape Canaveral in Florida.
NASA Explorer 1 - The Beginning of the Space Age (License: NASA Public Domain)
NASA Explorer 1 Launch (License: Creative Commons WM)
October 1, 1958
NASA is formed after Congress passes the National Aeronautics and Space Act.
October 11, 1958
NASA launches its first spacecraft, Pioneer 1, a Thor-Able space probe.
Pioneer 1 - United States Space Explorations 1958 pt1 (License: Creative Commons WM)
December 18, 1958
Launch of "SCORE" (Signal Communications by Orbiting Relay Equipment) communications payload. Atlas 10B/SCORE, the first voice relay satellite, was used to relay President Eisenhower's Christmas message which was the first voice transmitted from space.
1959
Mercury program launched (1959 - 1963)
Project Mercury was the Unites States first human spaceflight program and its goal was to put a human into orbit around the Earth. The program included 20 unmanned launches, followed by two suborbital and four orbital flights with astronaut pilots.
Pioneer 4 (License: Creative Commons WM)
Project Mercury Project (License: Creative Commons WM)
March 3rd, 1959
Pioneer 4 launched to the Moon, successfully completing the first US lunar fly-by returning radiation data.
1960
Nov 8, 1960
First flight of a production Mercury spacecraft. Little Joe 5 was launched from Wallops Island, Virginia. Sixteen seconds after liftoff, the escape rocket and the tower jettison rocket both fired prematurely. Also, the booster, capsule and escape tower failed to separate as intended.
Project Mercury-Redstone 1 Launch - 1960 NASA Educational Documentary (License: NASA Public Domain)
1961
May 5, 1961
With the launch of Freedom 7, Alan Shepard becomes the first American man in space. The suborbital flight, which was part of the Mercury Project, lasted 15 minutes, 28 seconds.
Launch of Freedom 7 with Alan Shepard (License: NASA Public Domain)
May 25, 1961
U.S. President John F. Kennedy, in response to political pressure resulting from Russia's successful launch of Sputnik 1, announces the goal of sending astronauts to the moon before the end of the decade.
John F. Kennedy's Moon Speech to Congress (License: Creative Commons)
Apollo program launched (1961 - 1972)
Commencement of the Apollo program which was created to achieve the national goal of 'landing a man on the Moon and returning him safely to the Earth'. The program operated from 1961 to 1972.
1962
1963
May 15, 1963
Faith 7 sends astronaut Gordon Cooper into space and he becomes the first American to spend over a day in space. Total flight time was 1 day, 10 hours and 19 mins.
Flight of Faith 7 (License: AV Geeks granted permission to use this video)
Gemini Program Launched (1963 - 1965)
Gemini program initiated to develop space travel techniques in support of the Apollo missions. The program ran between 1963 and 1966 and resulted in ten manned flights.
1964
April 8, 1964
First test flight of the Gemini program. It did not have humal life support systems. Although it featured a heat shield, the shield had four large holes drilled in it to make sure that the spacecraft was destroyed during reentry. In place of the crew couches were measuring equipment that relayed telemetry measuring the pressure, vibration, acceleration, temperature, and structural loads during the short flight.
1965
January 19, 1965
Gemini II suborbital flight to test heat shield. Shortly after launch the Mission Control Center suffered a power outage. Control of the mission was transferred to a tracking ship. The outage was later traced to an overload of the electrical system from the network television equipment used to cover the launch.
Gemini 2 Re-entry Mission 1965 NASA Educational Documentary (License: NASA Public Domain)
March 23, 1965
Gemini III first manned flight of the Gemini program. The spacecraft, nicknamed Molly Brown, performed the seventh manned US spaceflight and was the final manned flight controlled from Cape Canaveral, Florida before mission control functions were shifted to the Manned Spacecraft Center in Houston, Texas.
Gemini 3 First ever Spacewalk (License: NASA Public Domain)
Gemini 3 Spacewalk Training NASA Educational Documentary (License: Discovery Creative Commons)
June 3-7, 1965
Gemini IV first space walk. The second piloted Gemini mission stayed aloft for four days and astronaut Edward H. White II performed the first EVA or spacewalk by an American.
August 21, 1965
Launch of Gemini V, carrying astronauts Gordon Cooper and Charles Conrad on an eight-day mission to test rendezvous guidance and navigation systems, as well as study how humans could handle long-term exposure to a space environment. Gemini would be the critical link between the early Mercury Project and the Apollo missions.
December 15, 1965
Gemini VI-A successfully completes the first ever space rendezvous.
Gemini V1A Rendezvouz (License: Creative Commons)
1966
January 20, 1966
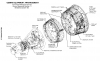
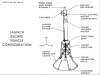
First fully operational test flights of the Launch Escape System (LES). LES consisted of a top-mounted rocket connected to the crew module of a crewed spacecraft and was used to quickly separate the crew module from the rest of the rocket in case of emergency.
LES Launch Escape System (License: Creative Commons)
March 16, 1966
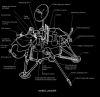
Gemini VIII manned by astronauts Scott and Armstrong, successfully complete the first docking with another space vehicle.
First Successful Docking with another Vehicle and First Emergency Landing (License: Creative Commons)
November 11, 1966
Gemini XII is the final flight of the Gemini program. Astronauts Lovell and Aldrin Rendezvoused and docked manually with its target and kept station with it during EVA. Aldrin set an EVA record of 5 hours 30 minutes for one space walk and two stand-up exercises, and demonstrated solutions to previous EVA problems.
1967
January 27, 1967
Mission AS-204 is struck by tragedy when a flash fire breaks out during a launch pad test, killing three astronauts: Virgil Grissom, who had participated in Mercury and Gemini flights; Edward White, who conducted NASA's first extravehicular activity; and new astronaut Roger Chaffee. The mission, one of NASA's first major setbacks, was later renamed Apollo 1.
AS-204 Disaster (License: Creative Commons)
November 9, 1967
First test flight of the Saturn V rocket, which would carry dozens of spacecraft into space in the years to come.
1968
January 22, 1968
Apollo 5 was the first unmanned test flight of the Lunar Module.
October 11, 1968
Apollo 7 was the first Apollo manned mission and orbited the earth for 11 days to test the Command Module which had been redesigned following the Apollo 1 fire.
Apollo 7 (License: Creative Commons)
December 21, 1968
Apollo 8, the second crewed mission in the Apollo space program, was the first human spaceflight to leave Earth orbit.
1969
July 16, 1969
Launch of Apollo 11, the mission that would fulfill President John F Kennedy's goal of reaching the Moon before the Soviet Union.
Apollo 11 Launch (License: NASA Public Domain)
July 20, 1969
Milestone for NASA - Astronauts Edwin "Buzz" Aldrin and Neil Armstrong become the first men to walk on the moon. Neil Armstrong said "That's one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind", just after stepping onto the Moon's surface.This was a big milestone for NASA
Apollo 11 Moon Landing (License: NASA Public Domain)
1970
April 11, 1970
Apollo 13 was launched. The lunar landing was aborted after an oxygen tank exploded two days later. Despite enormous problems caused by limited power, loss of cabin heat, shortage of potable water and the critical need to jerry-rig the carbon dioxide removal system, the crew returned safely to Earth on April 17. Commanded by James Lovell and also manned by John Swigert and Fred Haise.
Apollo 13 Houston We Have A Problem (License: NASA Public Domain)
Slow motion capture of Apollo 13 Launch from NASA Camera E72 (License: NASA Public Domain)
1972
March 2, 1972
The Launch of unmanned Pioneer 10 provided a bunch of firsts for the space program. Pioneer 10 and Pioneer 11 were robotic space probes. Pioneer 10 was launched in 1972 and its mission was to send back data and images of Jupiter. It was the first spacecraft to fly through the asteroid belt, fly to Jupiter and make close-up observations, Saturn, the Milky Way Galaxy and reach escape velocity to leave our Solar System. Pioneer 10 sent its last communication back to Earth on January 22, 2003, while 7.6 billion miles from home.
December 7, 1972
Apollo 17 was the final launch of the Apollo program. Mission commander Eugene Cernan was the last person to leave the Moon's surface.
Apollo 17 Orange Soil (License: NASA Public Domain)
Singing on the Moon (License: NASA Public Domain)
LROC Explores Apollo 17 Landing Site (License: NASA Public Domain)
Lift off from the Moon (License: NASA Public Domain)
1973
1975
July 15, 1975
Apollo-Soyuz Test Project is the first international manned space flight to test out cooperated space rescue and docking. This was the first joint U.S.- Soviet space flight.
Apollo Soyuz Test Project (License: NASA Public Domain)
August 20, 1975
Launch of Viking 1, the first orbiter and lander sent to Mars. Viking 2 would launch a few weeks later. Both landed safely on Mars and for six years sent back the first set of images and data from the Martian surface.
1977
August 12, 1977
ALT-12 - First free flight of the Space Shuttle. Enterprise was built for NASA as part of the Space Shuttle program to perform test flights in the atmosphere. It was constructed without engines or a functional heat shield, and was therefore not capable of spaceflight. It was originally planned to be named Constitution. A campaign by fans of the television show 'Star Trek' to President Gerald Ford asked that the orbiter be named after the Starship Enterprise, featured on the television show. Although Ford did not mention the campaign, the president said that he was "partial to the name" and overrode NASA officials.
Enterprise 747 Take off (License: Creative Commons)
August 20, 1977
Launch of Voyager 2, one of a pair of spacecraft sent by NASA on what was supposed to be a five-year mission to study Jupiter and Saturn. Voyagers 1 and 2 continue to send back pictures and data today, 30 years later from nearly 10 billion miles away.
September 5, 1977
Launch of Voyager 1. Voyager 1 would later return some incredible images from its encounter with Jupiter and Saturn.
1978
1981
April 12, 1981
STS-1 - Aboard the space shuttle Columbia, Robert L. Crippen and John W. Young make the first mission in NASA's Space Shuttle program. The Space Shuttle program (officially called Space Transportation System) ran from 1981 to 2011.
STS 1 Launch BBC Coverage (License: Creative Commons)
STS 1 NASA Shuttle Showcase (License: NASA Public Domain)
STS 1 Landing (License: NASA Public Domain)
STS 1 Launch Columbia Alternative View (License: NASA Public Domain)
STS 1 Launch Columbia (April 12, 1981) (License: NASA Public Domain)
1983
April 4, 1983
STS-6 - Challenger carries the first Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, TDRS-1, into orbit. Donald Peterson and Story Musgrave successfully accomplished the program's first extravehicular activity (EVA), performing various tests in the orbiter's payload bay. Their spacewalk lasted 4 hours and 17 minutes.
June 18, 1983
STS-7 - Sally Ride becomes first American woman in space with launch of shuttle mission STS-7 aboard the space shuttle Challenger.
August 30, 1983
STS-8 - Guion S. Bluford, Jr., becomes first African American in space with launch of shuttle mission STS-8 aboard the space shuttle Challenger. This is also the first ever night time landing of a Space Shuttle
1984
August 30, 1984
STS-41D - First flight of Space Shuttle Discovery. Mission included testing of the Solar Array and the deployment of three commercial communications satelites.
STS 41 D Discovery Mission Review (License: NASA Public Domain)
October 5, 1984
STS-41-G - First flight with two women in space, Sally Ride and Kathryn Sullivan. First spacewalk by a US woman (Sullivan). First Canadian in space. The on board IMAX camera filmed fottage for the IMAX movie, The Dream is Alive.
1985
1986
January 28, 1986
STS-51-L - First major catastrophe for NASA, when space shuttle Challenger exploded 73 seconds after takeoff with seven crew members aboard. Total loss of vehicle and crew, including a civilian teacher. It was later determined that the failure was caused by the failure of an O-ring seal on the Solid Rocket Boosters. 73 seconds after lift-off, the vehicle experienced a catastrophic structural failure and the orbiter rapidly broke up. The launch had been approved despite a predicted ambient temperature of 26 °F (−3 °C), well below the qualification limit of major components. It is almost certain the actual disintegration did not kill the entire crew as 3 of the 4 PEAPs (personal egress air packs) that were recovered had been manually activated.
Loss of Challenger 25 Years On (License: NASA Public Domain)
Loss of Challenger (License: NASA Public Domain)
February 19, 1986
Mir space station launches.
1988
September 29, 1988
STS-26 - Space Shuttle flights resume when Discovery is launced from Kennedy Space Center. It was declared the "Return to Flight" mission. The primary payload was a Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS). Eleven scheduled mid-deck scientific and technological experiments were carried out. The orbiter sustained only minor Thermal Protection System tile damage, and the redesigned post-Challenger solid rocket boosters showed no signs of leakage or overheating at any of the joints.
1989
October 18, 1989
STS-34 - Space shuttle Atlantis launches Galileo to study Jupiter and its moons. It took Galileo six years to reach Jupiter, and it finally disintegrated in Jupiter's atmosphere in September of 2003, 14 years after it began its collision course toward the giant planet.
Launch of Atlantis and Gallileo (License: NASA Public Domain)
Crew onboard Atlantis (License: NASA Public Domain)
1990
1993
December 19, 1993
STS-61 - This was the first Hubble Space Telescope servicing mission. The mission restored the spaceborne observatory's vision with the installation of a corrective optics package and also installed instrument upgrades. The STS-61 mission was one of the most complex in the Shuttle's history. It lasted almost 11 days, and crew members made five spacewalks, an all-time record.
STS 61 Hubble Space Telescope Recovery and Repairs (License: NASA Public Domain)
1994
1995
1997
1998
1999
July 22-27, 1999
STS-93 - First woman to command a Shuttle mission. Columbia's 26th flight was led by Air Force Col. Eileen Collins. Five seconds after launch an electrical short disabled the primary controller on two of the three main engines and they automatically switched to backup controllers. The problem was later discovered to have been caused by poorly routed wiring which had rubbed on an exposed screw head. Premature engine shutdown resulted in a slightly lower orbit.
2000
2001
August 8, 2001
Launch of Genesis, which would collect samples of atoms from solar wind which is ejected from the outer portion of the sun, and return it to Earth. Genesis would be the first attempt to return samples to Earth since the Apollo moon mission in 1972. Upon return to Earth it crash-landed in Utah on September 8, 2004, after a design flaw prevented the deployment of its parachute. Most of the samples were damaged but some were successfully recovered.
Nasa Genesis Capsule Spirals Out of Control and Crashes (License: NASA Public Domain)
2003
February 1, 2003
STS-107 - Crew of seven astronauts, including the first Israeli astronaut, is lost after a 16-day mission when the Columbia space shuttle explodes on re-entry. The accident was later attributed to damage sustained to foam insulation and has led NASA to understand how to safely repair similar damage on later missions.
George Bush addresses the Nation (License: Creative Commons)
WFAA Video of the break-up of Columbia (License: Creative Commons)
June 10 and July 7, 2003
Mars Exploration Rovers Spirit and Opportunity launch.
2004
January 2004
Spirit and Opportunity arrive on the Martian surface. They continue to explore the Red Planet today.
September 8, 2004
After capturing particles from the sun, Genesis makes a dramatic crash landing in Utah when its parachute fails to deploy. Despite the landing, scientists still managed to recover and study the samples.
Genesis Tumbling to Earth (License: NASA Public Domain)
2005
July 26, 2005
STS-114 - Space Shuttle Discovery launched successfully into orbit, marking NASA's first return to human spaceflight after the Columbia tragedy. The problem that caused the loss of Columbia – debris separating from the external tank during ascent – unexpectedly recurred during the launch of Discovery. As a result, NASA decided to postpone future shuttle flights pending modifications.
STS 114 (License: NASA Public Domain)
2006
2009
Various Shuttle missions to the ISS for assembly.
STS 127 Post Mission Presentation (License: NASA Public Domain)
STS 119 Launch (License: NASA Public Domain)
2010
2011
July 8, 2011
STS-135 - The launch of final flight of the Space Shuttle program. Atlantis carried a Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM) Raffaello and a Lightweight Multi-Purpose Carrier (LMC). Only four astronauts were assigned to this mission, versus the normal six or seven, because there were no other Space Shuttles available for a rescue following the retirement of Discovery and Endeavour.
July 21, 2011
Landing of STS-135 and the end of the Space Shuttle era. STS-135 delivered supplies and equipment to provision the space station through 2012, following the end of NASA's space shuttle program.
STS 135 Landing (License: NASA Public Domain)
STS 135 The Final Landing of the Space Shuttle (License: Spacevidcast Creative Commons)
Approximately 115 tons of ocean salt spray enters the earth's atmosphere each second.