Private Sector Space Companies
NASA's Commercial Crew Program

NASA administers an investment initiative, on behalf of the U.S. Government, called the "Commercial Crew Program". Through this initiative funds are awarded to companies in the private sector that are committed to the development of spacecraft with the goal of achieving safe, reliable, and cost effective access to and from low-Earth orbit and the International Space Station (ISS).
Through this development and certification process, NASA will help lay the foundation for future commercial transportation capabilities. Once a transportation capability is certified for NASA use, NASA could purchase transportation services to meet its ISS crew rotation and emergency return obligations.
Requirements
The key high-level requirements for the Commercial Crew vehicles include:
- Deliver and return four crew members and their equipment.
- Provide assured crew return in the event of an emergency.
- Serve as a 24-hour safe haven in the event of an emergency.
- Capable of remaining docked for 210 days.
Commercial Funding Recipients
Companies to date that have received NASA funding are:
- Blue Origin, Kent, Washington
- Sierra Nevada Corporation, Louisville, Colorado
- Space Exploration Technologies (SpaceX), Hawthorne, California
- The Boeing Company, Houston, Texas
SpaceX
SpaceX, or Space Exploration Technologies Corporation, was founded in June 2002 by PayPal and Tesla Motors co-founder Elon Musk. The company has grown rapidly since it was founded in 2002, growing from 160 employees in November 2005 to more than 1,700 in 2011. It's headquarters are in Hawthorne, California.
It has developed the Falcon 1 and Falcon 9 space boosters, both of which are built with a goal of becoming reusable launch vehicles. SpaceX is also developing the Dragon spacecraft.
In 2006, NASA awarded the company a contract to design and demonstrate a launch system to resupply cargo to the International Space Station (ISS) and on 9 December 2010, the launch of the Demo Flight 1 mission, SpaceX became the first privately funded company to successfully launch, orbit and recover a spacecraft.
NASA has also awarded SpaceX a contract to develop and demonstrate a human-rated Dragon as part of its Commercial Crew Development (CCDev) program to transport crew to the ISS.
Blue Origin
Blue Origin is a privately funded aerospace company set up by Amazon.com founder Jeff Bezos. Its headquarters is located in Kent, Washington. The company has been notoriously tight-lipped about its plans. Although the company was incorporated in 2000, its existence only became public in 2003, when Bezos started buying land in Texas.
NASA awarded the company $3.7 million in funding under the Commercial Crew Development in 2010. They received another $22 million during the second phase of the Commercial Crew Development program as NASA was particularly interested in their "pusher" Launch Abort System as all others to date have "pulled" crew to safety.
Initially focused on sub-orbital spaceflight, the company has built and flown a test-bed of its New Shepard spacecraft design at their Culberson County, Texas facility.
In a 2011 interview, Bezos indicated that he founded the company to help enable "anybody to go into space" and that to do so, he must focus on two objectives: thus, the mission of Blue Origin is to decrease the cost of access to space and increase the safety of human spaceflight.
Blue Origin has also started work on developing systems for an orbital spacecraft that would be launched atop an Atlas V 402.
Sierra Nevada Corporation

Sierra Nevada Corporation (SNC) is an electronic systems provider. On December 16, 2008 SNC announced it had completed its acquisition of SpaceDev. The company contracts with the US military, NASA and private spaceflight companies and is headquartered in Sparks, Nevada. SpaceDev is based near San Diego in Poway, California. The company's objective is to make routine commercial spaceflight possible and to help open space for all of humanity.
The company is developing an orbital spacecraft called the Dream Chaser. In February 2010, SNC was awarded $20 million in phase 1 of NASA's Commercial Crew Development program for the development of the Dream Chaser. SNC is also developing micro-satellites and nano-satellites, a small expendable launch vehicle, the SpaceDev Streaker.
The Boeing Company
The Boeing Company is an American multinational aerospace and defense corporation, founded in 1916 by William E. Boeing in Seattle, Washington. Boeing Corporate headquarters has been in Chicago, Illinois since 2001. Boeing Space Exploration, headquartered in Houston, is a leading provider of human spaceflight and space exploration systems and services having participated in the X-15, Gemini, Mercury, Apollo and Skylab, Space Launch System, International Space Station.
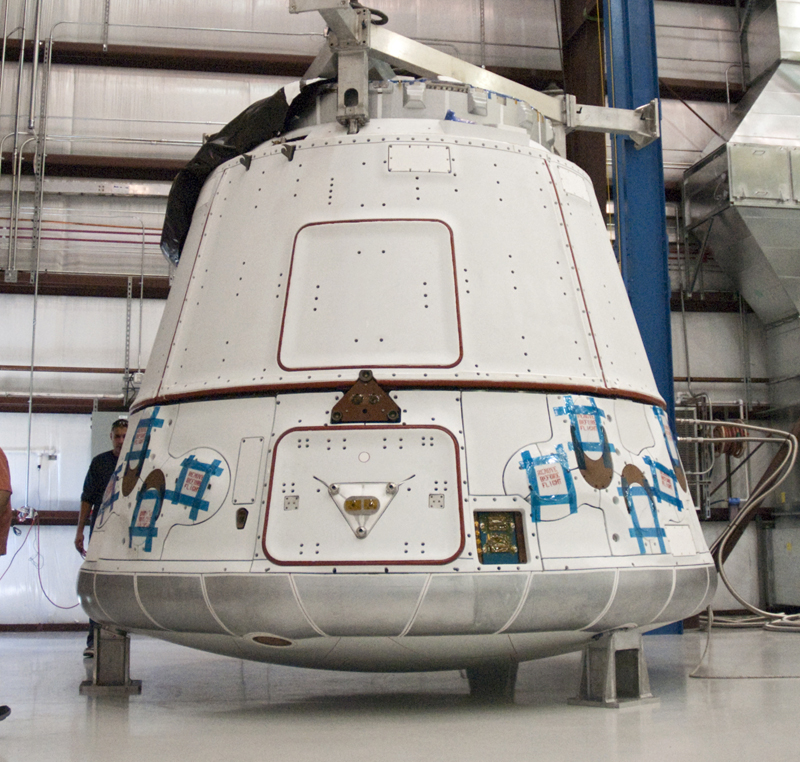
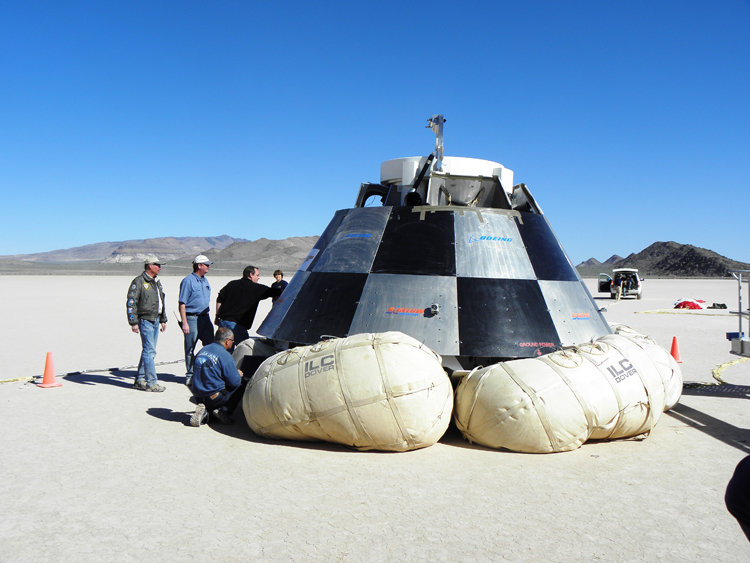
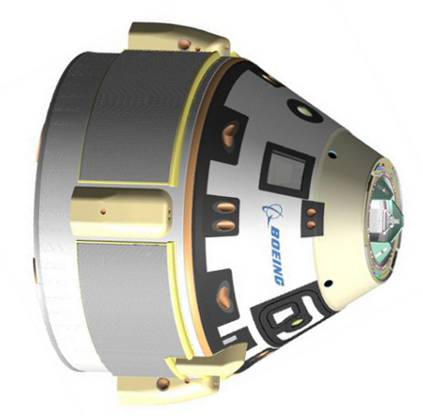
Boeing's Commercial Crew Transportation System (CCTS) includes the CST-100 spacecraft, launch services and ground systems. The CST-100 is a reusable spacecraft that has a crew module and service module. Its primary mission would be to transport crew to the International Space Station. Outwardly it would look much like the Orion, a spacecraft being built for NASA by Lockheed Martin. The CST-100 would be able to support larger crews of up to 7 people
In the first phase of its CCDev program NASA awarded Boeing $18 million for preliminary development of the spacecraft. In the second phase Boeing was awarded $93 million.
Virgin Galactic

Virgin Galactic is planning to make suborbital flights, and travel around the globe. They also will offer space hotels and trips to the moon. The suborbital flight tickets will cost $200,000 for each seat! They have a plan for at least 50,000 people to visit space over the next ten years.
The vice president, Alex Tai, wants to fly the first flight as one of the pilots. Tai said it was about seven minutes of black sky, four minutes of zero gravity, and training to be an astronaut.
Virgin Galactic also wants to build multiple reusable private spaceships. They had made a deal for $1.6 million to start launching scientists into space. Virgin Galactic's main goal is to make space travel possible to almost anyone. They will check a passengers health before liftoff. The medical checks will not be restrictive so people who want to go on the flight aren't restricted by health problems. They tested a group of people under the G-forces that are expected in flight. 93% of the people passed the medical test.
← Exploration International Space Station →
An unprotected human can survive up to 1.5 minutes in space with no permanent bodily damage.